Porter’s 5 forces Analysis is a model of analysis that helps to explain why different industries are able to sustain different levels of profitability. It is named after Michael analyzing the level of competition within an industry and business strategy Porter, a famous economist from Harvard Business School.This framework helps in development.
So what are they ?
The Five forces are :
- Threat of new entrants
- Threat of substitutes
- Bargaining Power of customers
- Bargaining Power of buyers
- Competitive Rivalry
These are the five competitive forces that shape every industry, and helps determine an industry's weaknesses and strengths. This model was developed in reaction to SWOT analysis which many people felt was not rigorous enough.
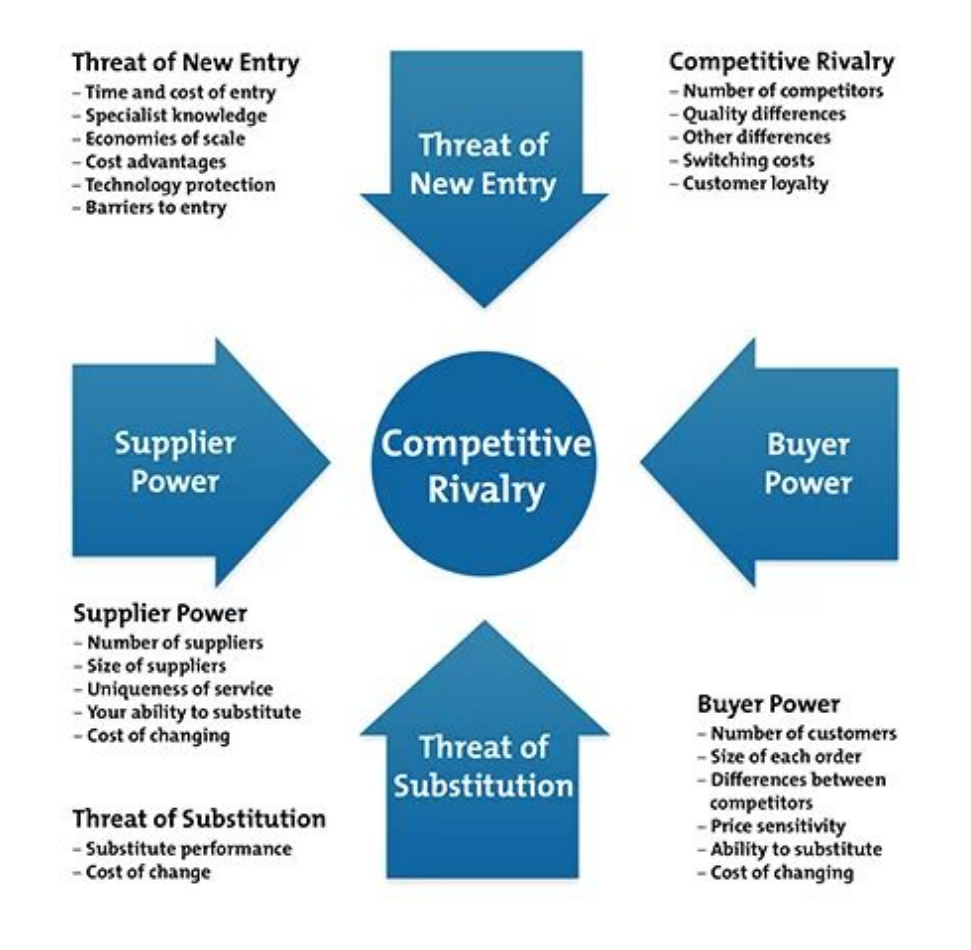
Threat of New Entrants
The force of new entrants into a market affects a company's power.It measures how easy or difficult it is for competitors to join the marketplace in the industry being examined. The easier it is for a competitor to join the marketplace, the greater the risk of a business's market share being depleted.
Bargaining power of Suppliers
This force addresses how easily suppliers can drive up the price of goods and services in other words how much power a business's supplier has and how much control it has over the potential to raise its prices, which, in turn, would lower a business's profitability because a supplier to gain a profit will try to increase its selling price which thereby would cause an increase in the cost price thereby decreasing the profits. In addition, it looks at the number of suppliers available: The fewer there are, the more power they have.
Bargaining power of Customers
This specifically deals with the ability of customers have to drive prices down. It is affected by how many buyers, or customers, a company has.Consumers have power when there aren't many of them, but lots of sellers, as well as when it is easy to switch from one business's products or services to another. The smaller and more powerful a client base, the more power it holds. Buying power is low when consumers purchase products in small amounts and the seller's product is very different from any of its competitors.
Threat of Substitutes
The substitutions that can be used in place of a company's products or services pose a threat. For example, if customers rely on a company to provide a tool or service that can be substituted with another tool or service or by performing the task manually, and this substitution is fairly easy and of low cost, a company's power can be weakened.
Competitive Rivalry
The importance of this force is the number of competitors and their ability to threaten a company. The larger the number of competitors, the larger is the rivalry. This force examines how intense the competition currently is in the marketplace, which is determined by the number of existing competitors and what each is capable of doing. Rivalry competition is high when there are just a few businesses equally selling a product or service and when rivalry competition is high, advertising and price wars can follow.
In order to understand it better, here is an example :
Porter's analysis on Pizza hut
Intensity of Competitive rivalry: HIGH
- There is definitely intense competition that Pizza hut constantly faces from other fast food chains especially McDonald’s, KFC, Dominos etc.
- Fierce price discounting, coupons, fast home deliveries and special customer offers have intensified the competition.
- Apart from these established competition, there is a stiff competition from local pizza restaurants as well who provide pizzas faster and at a cheaper rate.
- There are other substitutes also available to pizza market such as the local super markets who not only provide frozen pizzas but also sell ready to bake pizzas and often large size pizza which is a major setback for Pizza hut.
Threats of Substitutes: HIGH
- Dominos pizza is the highest competitive substitute to Pizza hut because it provides almost the same pizzas and other fast food products.
- There are many other options available for pizzas such as US pizza, Papa Jones, California Pizza Kitchen which ensures a high cross price elasticity and makes it difficult for pizza hut to raise prices.
- Not only pizzas, but there are other substitutes also available in the junk food market like KFC, Wendy’s and other sandwich chains, chicken fast food chains,family restaurants etc.
- ● The quickly growing demands for the packed food and ready to bake junk items including pizzas are absorbing a lot of customers from pizza chains as a whole.
- Thus, the threat of substitutes highly influence on price, its elasticity is high as customers have various alternatives available.
Threats of new entrants: LOW
- For a new pizza chain, pizza industry is not a doddle. Pizza chains suffer huge recession due to increased ingredient prices, slim margins and stiff competition.
- An already existing chain like Pizza hut has a winover advantage over the new competitor in this respect as they have improved technology, resources and experiences.
- Mostly, the relationships with the suppliers matters a lot in a pizza industry that helps to keep the cost of production low so as to increase the productivity.
- Moreover, customers are loyal to the existing brand “Pizza hut” which is very well doing in order to satisfy its customers and maintain the brand image.
- Most of the “Patents” acquired by Pizza Hut cover most of the latest technologies to let it available for some new entrant.
Bargaining Power of Customers: LOW
- Fast food consumers are large in number and most of them rely on the brand.
- Every single customer is unlikely to purchase a large amount of pizzas, so a single customer or a certain section of it does not influence a lot to the overall sales.
- QSRs are a lot in demand especially in malls, colleges, office arenas etc. So pizzas are quite inelastic to the price fluctuations with these section of people.
- So, overall these pizza freak customers are segmented has a low bargaining power.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers : LOW
- There is a huge diversified supply chain available for Pizza hut for its ingredients and raw materials.
- Supplier’s don’t find themselves in a strong bargaining position as the core ingredient for the this food industry are the commodity products easily available such as flour, cheese, sauce etc.
- Labours is also abundant for this labour intensive industry.
- Suppliers tend to keep long term relationships with the purchasers thereby making it easier for the purchasers(pizza hut) to negotiate on lesser prices.
